In the evolving world of decentralized finance (DeFi), Token Staking has emerged as one of the most accessible and rewarding ways for crypto holders to grow their assets. As blockchain networks increasingly rely on Proof of Stake (PoS) and its variants, token staking has transitioned from a niche concept into a core component of the crypto economy.
But what exactly is token staking? How does it work? And why has it become such an integral part of the digital asset landscape? This article provides a deep dive into token staking, exploring its benefits, risks, mechanisms, and role in securing blockchain networks.
What Is Token Staking?
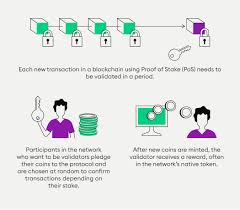
Token staking refers to the process of actively participating in a blockchain network’s consensus mechanism by locking up a specific amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet to support network operations such as validating transactions and securing the protocol.
In return for staking their tokens, participants receive rewards—typically in the form of additional tokens. These rewards act as an incentive for users to maintain the integrity and security of the blockchain.
Staking is primarily associated with Proof of Stake (PoS) and its variations such as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS), and Liquid Staking.
How Token Staking Works
- Locking Tokens
Users lock (or “stake”) their tokens in a staking wallet or on a staking platform for a set or flexible period. - Validating Transactions
Stakers, also known as validators or delegators (depending on the model), participate in verifying new blocks of transactions. In PoS systems, validators are chosen based on the number of tokens staked and other factors such as staking duration or randomness. - Earning Rewards
Participants earn rewards based on their stake and the performance of the validator node. These rewards are often paid in the same token being staked. - Unstaking Period
Many blockchains have an “unstaking” or “cool-down” period during which tokens cannot be transferred or withdrawn.
Benefits of Token Staking
- Passive Income: By staking tokens, holders can earn regular rewards without needing to trade actively.
- Network Participation: Stakers contribute to the decentralization and security of the blockchain.
- Eco-Friendly Alternative: PoS and staking require significantly less energy than traditional Proof of Work (PoW) mining.
- Incentive Alignment: Stakers are financially incentivized to act honestly, aligning their interests with the network’s health.
Popular Platforms and Blockchains for Staking
- Ethereum 2.0 (ETH): Since its transition to PoS, staking ETH has become central to network security.
- Cardano (ADA): Uses a unique PoS model called Ouroboros, allowing users to delegate to pools.
- Polkadot (DOT): Employs Nominated Proof of Stake, where nominators support validators.
- Solana (SOL): Offers fast transaction finality and staking through validators and staking pools.
- Cosmos (ATOM): A hub-and-zone ecosystem with staking as a security cornerstone.
Platforms like Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, and Lido offer user-friendly staking services for those who prefer not to manage nodes themselves.
Risks and Considerations
While staking is often viewed as a low-risk, passive strategy, it’s not without potential downsides:
- Slashing: Validators can be penalized for bad behavior (e.g., downtime or malicious activity), leading to a partial loss of staked funds.
- Lock-Up Periods: During unstaking, assets may be illiquid, which could lead to opportunity loss during market volatility.
- Centralization Risk: Some staking pools grow disproportionately large, undermining decentralization.
- Platform Risks: Using third-party platforms for staking introduces custodial risks, including platform hacks or mismanagement.
Strategies to Maximize Staking Rewards
- Research Validators: Choose validators with good performance, low fees, and active participation.
- Diversify Staking: Spread your tokens across different platforms or blockchains to mitigate risks.
- Reinvest Rewards: Compounding your rewards can accelerate the growth of your staked assets.
- Use Liquid Staking: Platforms like Lido offer liquid staking tokens (e.g., stETH), enabling users to earn rewards while retaining liquidity.
The Future of Token Staking
Token staking is poised to grow alongside the broader adoption of blockchain technology. As Ethereum finalizes its PoS transition and more Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks implement staking incentives, the demand for secure, scalable staking solutions will continue to rise.
Moreover, staking is becoming a critical bridge between traditional finance and DeFi. Institutional investors are entering staking markets, drawn by attractive yields and network participation opportunities. Regulatory clarity in this space will further enhance trust and scalability.
Conclusion
Token staking represents a powerful fusion of participation and reward in the decentralized ecosystem. It allows users to earn passive income while actively contributing to blockchain security and decentralization. As the crypto industry continues to mature, staking is evolving from a technical process into a mainstream investment strategy.
Whether you’re a casual investor or a blockchain enthusiast, understanding and leveraging token staking can be a smart move in the digital age. With proper research and risk management, staking offers a rewarding path to grow your crypto portfolio and support the technologies shaping the future.








Leave A Reply