In recent years, the financial landscape has witnessed a transformative shift toward digitalization, with virtual tokenized assets leading the charge. These assets—ranging from real estate and art to commodities and equities—are being converted into digital tokens on the blockchain, creating new opportunities for investors and reducing barriers to asset ownership. But what exactly are virtual tokenized assets, how do they work, and what are their implications for the future of finance and investment?
In this article, we’ll explore the concept of virtual tokenized assets, their benefits, challenges, and how they are reshaping the global economy.
What Are Virtual Tokenized Assets?
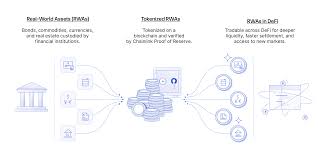
Virtual tokenized assets refer to real-world or digital assets that are represented by a blockchain-based token. These tokens act as a digital representation of ownership, and the underlying asset can be anything from real estate, gold, and artwork to more intangible assets like intellectual property or even a share in a company. By tokenizing these assets, they are divided into smaller units, allowing for fractional ownership, easier transferability, and improved liquidity.
Tokenization involves converting the rights and ownership of an asset into a digital format using smart contracts on a blockchain. This process can make traditionally illiquid or hard-to-trade assets more accessible and easier to trade on decentralized markets. Essentially, tokenization is about bringing real-world assets onto the blockchain for easier management and trading.
How Virtual Tokenized Assets Work
The process of creating virtual tokenized assets is relatively straightforward but relies heavily on blockchain technology to ensure security and transparency. Here’s how it typically works:
- Tokenization: A real-world asset (like a property or artwork) is chosen for tokenization. The asset is then represented as digital tokens on a blockchain, which reflect the value of the asset.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are used to define the terms of ownership, rights, and any associated transactions. These contracts are immutable and decentralized, making them transparent and secure.
- Fractional Ownership: The asset is often divided into multiple tokens, allowing investors to own a fraction of the asset rather than having to buy it entirely. This opens up investment opportunities to a broader audience.
- Trading on Blockchain: Once the asset is tokenized, it can be traded on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or digital marketplaces. Because the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it provides a secure, transparent, and efficient way to buy and sell tokens.
- Settlement: Once a transaction is made, settlement occurs almost instantly, without the need for intermediaries, reducing fees and delays typical in traditional financial systems.
Benefits of Virtual Tokenized Assets
- Increased Liquidity: Traditionally, many assets (such as real estate, fine art, or rare collectibles) are illiquid and difficult to trade. By tokenizing these assets, investors can easily buy, sell, or trade fractions of them, significantly enhancing liquidity.
- Fractional Ownership: Tokenization enables fractional ownership, meaning that individuals can invest in assets that would otherwise be out of their reach. For example, one can own a fraction of a multi-million-dollar painting or a luxury property, thereby lowering the entry barriers for small investors.
- Global Accessibility: Tokenized assets can be traded globally, 24/7, without the constraints of geographical borders. This democratizes access to assets and enables investors from around the world to participate in markets that were previously unavailable to them.
- Reduced Transaction Costs: Blockchain technology enables peer-to-peer transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries, such as brokers or banks, thereby cutting down transaction fees and processing times.
- Transparency and Security: Blockchain provides a transparent and immutable ledger, ensuring that ownership records are secure, verifiable, and resistant to tampering. This gives investors confidence that their assets are genuine and well-documented.
Applications of Virtual Tokenized Assets
- Real Estate: Tokenized real estate is one of the most promising areas for blockchain adoption. Tokenization allows fractional ownership of properties, reducing the capital required for investment. Real estate investment platforms like RealT and Slice have already started offering tokenized property investments.
- Art and Collectibles: High-value art and collectibles can be tokenized, allowing smaller investors to own a fraction of a piece of rare art. Platforms like Maecenas and CurioInvest are paving the way for tokenized art investments.
- Commodities and Precious Metals: Tokenizing commodities like gold, silver, and oil makes these markets more accessible and easier to trade, providing investors with a way to diversify their portfolios without owning the physical assets.
- Equities and Bonds: Tokenized stocks or bonds represent shares in a company or debt instruments, allowing for the trading of traditional financial assets in a decentralized way. Security token offerings (STOs) are becoming a popular way for companies to raise capital.
- Intellectual Property and Patents: Intellectual property rights, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights, can also be tokenized. This allows creators to monetize their intellectual property in new ways, and investors can buy, sell, or trade tokens tied to IP rights.
Challenges and Risks of Virtual Tokenized Assets
While virtual tokenized assets offer a wide range of benefits, they are not without challenges and risks:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape surrounding tokenized assets is still evolving. Governments and financial regulators are working to define how tokenized assets fit within existing legal frameworks, which can create uncertainty for investors.
- Technology Risks: The security of blockchain platforms is crucial. While blockchain is inherently secure, the technology surrounding smart contracts, wallets, and exchanges can be vulnerable to hacking or bugs.
- Market Volatility: Like cryptocurrencies, tokenized assets can experience high volatility. This can lead to substantial risks for investors, especially if the market is not well-established or lacks liquidity.
- Lack of Standardization: The lack of universal standards for tokenization across different industries may result in inconsistencies in how assets are represented and traded, potentially hindering adoption.
Conclusion
Virtual tokenized assets are undoubtedly reshaping the future of investment and asset management. By enabling fractional ownership, increasing liquidity, and offering global accessibility, tokenized assets are opening new doors for both investors and asset owners. However, as with any emerging technology, challenges remain, particularly in terms of regulation and market volatility.
As blockchain technology matures and regulatory frameworks develop, the adoption of tokenized assets will likely grow, providing investors with innovative and exciting ways to diversify their portfolios. Virtual tokenized assets have the potential to revolutionize not just how we invest, but how we think about ownership and value in the digital age.








Leave A Reply