In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, Proof of History (PoH) has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, particularly with its implementation in the Solana blockchain. Unlike traditional consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), Proof of History offers a unique way to verify transactions and secure decentralized networks. This article explores what Proof of History is, how it works, and why it’s important in the context of blockchain technology.
What is Proof of History?
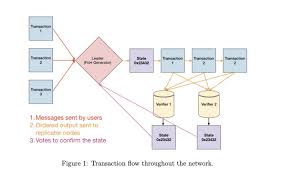
Proof of History (PoH) is a consensus algorithm that uses cryptographic techniques to create a historical record that proves that an event has occurred at a specific moment in time. Unlike other consensus models, PoH doesn’t require validators to communicate and agree on the order of transactions, making it faster and more scalable.
Proof of History creates a verifiable timeline of events, which helps decentralize the process of confirming transactions. It’s often used in combination with other consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS), to ensure network security and efficiency. One of the most notable blockchains using Proof of History is Solana, which has gained attention for its ability to handle thousands of transactions per second with low fees.
How Does Proof of History Work?
At its core, Proof of History is based on the idea of creating a sequence of events that can be used to verify the passage of time without requiring all participants in the network to agree on the exact time. This is done using a verifiable delay function (VDF).
Here’s a simplified explanation of how Proof of History works:
1. Timestamping Events with a Verifiable Delay Function (VDF)
Proof of History creates a cryptographic proof that records the time between two events. This is achieved through a VDF, which generates a sequence of numbers in a way that it’s difficult to predict but easy to verify once completed. The output of the VDF is a timestamp that serves as proof that a specific event occurred at a certain time.
For instance, when a transaction occurs, the blockchain records the time the event happens through this timestamp. This timestamp is then verified by other nodes in the network, providing the proof that the event occurred in the correct order and at the correct time.
2. Efficiency and Speed
One of the key benefits of Proof of History is its ability to streamline the process of transaction verification. In traditional systems like Proof of Work (PoW), miners or validators must work to agree on the sequence of events. This process takes time and resources. However, with PoH, the timestamp for each event is already embedded within the transaction data, reducing the need for constant communication between validators.
This makes Proof of History a much more efficient and faster method of consensus, significantly increasing transaction throughput. Solana, for example, can handle over 65,000 transactions per second (TPS), far exceeding Bitcoin and Ethereum.
3. Integration with Proof of Stake (PoS)
In networks like Solana, Proof of History is combined with Proof of Stake (PoS) to further enhance security. While PoH timestamps the transactions, PoS ensures that only legitimate validators participate in securing the network. Validators are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are incentivized to act honestly to maintain their stake.
This hybrid approach ensures that the network remains both fast and secure, leveraging the best of both consensus models.
Benefits of Proof of History
1. Scalability
The primary advantage of Proof of History is its scalability. By eliminating the need for constant communication between nodes to agree on transaction order, PoH significantly speeds up transaction processing. This scalability is essential as blockchain networks need to handle a growing number of users and transactions without compromising performance.
For instance, Solana’s ability to process thousands of transactions per second is made possible by PoH, allowing it to compete with traditional payment systems like Visa in terms of transaction throughput.
2. Lower Costs
Proof of History helps reduce the cost of transactions on the network. Since PoH doesn’t require constant validation from miners or validators, there is less computational overhead. This reduction in computational demand translates to lower transaction fees, which is a significant benefit for users who rely on blockchain networks for everyday transactions.
3. Security and Decentralization
PoH also enhances the security and decentralization of blockchain networks. By creating a verifiable history of events, Proof of History ensures that all transactions are time-stamped and immutable. This cryptographic proof makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to alter the transaction history, ensuring data integrity and preventing fraud.
Moreover, because PoH does not rely on a central authority for validating transactions, it keeps the network decentralized. The absence of intermediaries and reliance on cryptographic proofs ensures that no single entity can control the blockchain, making it more resilient to attacks.
Use Cases of Proof of History
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
One of the most prominent use cases for Proof of History is in Decentralized Finance (DeFi). DeFi platforms require fast, secure, and transparent transaction processing to facilitate lending, borrowing, trading, and other financial services. Solana, which utilizes PoH, is a popular platform for DeFi applications due to its low fees and high transaction speed.
2. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Another area where Proof of History is gaining traction is in the NFT market. NFTs, which are unique digital assets tied to a specific blockchain transaction, benefit from the immutability and time-stamping features provided by PoH. This ensures the authenticity and provenance of NFTs, making it harder for counterfeiters to create fake digital assets.
3. Supply Chain Tracking
Proof of History is also being explored in supply chain management. By providing a transparent and verifiable timeline for goods and products as they move through the supply chain, PoH can ensure that each step is recorded and timestamped. This level of transparency helps prevent fraud and ensures the integrity of the supply chain.
Challenges and Limitations of Proof of History
While Proof of History offers numerous benefits, there are some challenges and limitations to consider:
1. Centralization Risks
Although PoH enhances decentralization in many ways, the hybrid nature of combining PoH with PoS can potentially lead to centralization. If a small number of validators hold a significant portion of the cryptocurrency supply, they may exert disproportionate control over the network, which could undermine the decentralization benefits.
2. Energy Consumption
Although PoH is more energy-efficient compared to Proof of Work, it still requires significant computational resources, especially when processing large volumes of transactions. As blockchain adoption continues to rise, the energy consumption of PoH networks may become a concern, particularly with growing environmental awareness.
Conclusion
Proof of History is an innovative consensus mechanism that brings scalability, security, and efficiency to blockchain networks. By providing a unique way to timestamp transactions, PoH reduces the need for constant communication between nodes, making blockchain networks faster and more scalable. Combined with Proof of Stake, it ensures both security and decentralization, which are key for the long-term success of blockchain technology.
As blockchain continues to evolve, Proof of History has the potential to shape the future of decentralized applications, DeFi, and beyond. With platforms like Solana already demonstrating the power of PoH, this consensus model is well on its way to revolutionizing the way blockchain networks operate.








Leave A Reply