Introduction
In the age of digital transformation, traditional methods of data storage and management are increasingly being replaced by more innovative solutions. One such groundbreaking technology is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). DLT is a decentralized database system that records transactions and data across multiple locations, providing greater transparency, security, and efficiency. While most commonly associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, the potential applications of distributed ledgers extend far beyond digital currencies.
This article will explore the concept of Distributed Ledger Technology, how it works, its benefits, challenges, and the various industries it is transforming. By understanding the importance of DLT, you can gain valuable insights into its potential to revolutionize data management and beyond.
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
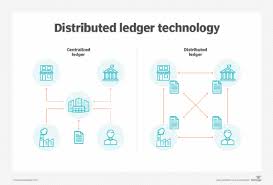
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) refers to a type of database that is spread across multiple locations or participants, eliminating the need for a central authority. Unlike traditional centralized databases, where one entity controls the data, DLT enables participants to independently verify and store data. This makes DLT highly secure, transparent, and resistant to tampering.
The most well-known example of DLT is blockchain, which is used in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. However, not all distributed ledgers are blockchains. While a blockchain is a type of distributed ledger that records data in blocks linked together in a chain, other types of distributed ledgers may use different structures and consensus mechanisms.
Key Characteristics of Distributed Ledgers:
- Decentralization: Data is stored across multiple locations, with no central authority controlling it.
- Transparency: Transactions are visible to all participants in the network.
- Security: The decentralized nature makes it highly resistant to hacking and tampering.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on a distributed ledger, it cannot be changed, providing a high level of data integrity.
How Does Distributed Ledger Technology Work?
At its core, DLT involves a network of computers (nodes) that are all interconnected. These nodes work together to verify and record transactions or data updates, ensuring that all participants in the network have access to the same information. The consensus mechanism is a key component of DLT, as it ensures that all participants agree on the validity of a transaction before it is added to the ledger.
For example, in blockchain-based systems like Bitcoin, a process called mining is used to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. In non-blockchain DLT systems, other consensus algorithms such as Proof of Stake (PoS), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) may be employed.
Once a transaction is validated by the network, it is recorded on the ledger, making it visible and accessible to all participants. The immutability of the ledger means that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity of the system.
Benefits of Distributed Ledger Technology
DLT offers numerous advantages over traditional centralized systems. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Increased Security
The decentralized nature of DLT makes it inherently more secure than traditional centralized databases. Since the data is distributed across multiple nodes, it is much harder for a single point of failure to compromise the system. Additionally, DLT systems often employ cryptographic techniques to secure data, making it highly resistant to fraud and hacking.
2. Enhanced Transparency
All participants in a distributed ledger network have access to the same data, ensuring complete transparency. This transparency is particularly beneficial for industries that require trust and accountability, such as finance and supply chain management. In a blockchain-based system, for instance, all transactions are publicly recorded and can be easily verified by anyone on the network.
3. Reduced Costs and Improved Efficiency
Traditional centralized systems often require intermediaries, such as banks, notaries, or third-party verification services, to facilitate transactions and maintain data integrity. These intermediaries come with associated costs and inefficiencies. DLT eliminates the need for intermediaries by allowing direct peer-to-peer transactions, which can significantly reduce costs and speed up processes.
4. Improved Data Integrity and Immutability
Once data is recorded on a distributed ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted without the consensus of the network. This makes DLT ideal for applications that require high levels of data integrity, such as legal contracts, financial transactions, and medical records. The immutability of the ledger ensures that historical data remains accurate and unaltered.
5. Decentralization and Autonomy
DLT allows for a decentralized, autonomous system where no single entity has full control. This decentralization removes the risks associated with centralized authorities, such as censorship, fraud, or corruption. It empowers participants and provides a more equitable system for all users.
Use Cases of Distributed Ledger Technology
Distributed ledger technology has far-reaching applications across various industries. Below are some notable examples:
1. Cryptocurrencies and Digital Payments
The most famous application of DLT is cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain technology to record and verify transactions. By using a decentralized ledger, cryptocurrencies allow for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a central authority such as a bank or payment processor.
2. Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, DLT can be used to track the movement of goods and verify the authenticity of products. By recording each step of the supply chain on a distributed ledger, companies can ensure the integrity of their products and provide consumers with proof of origin. This has become particularly important in industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where provenance and quality control are crucial.
3. Voting Systems
DLT has the potential to revolutionize voting systems by providing a secure and transparent platform for elections. Using a distributed ledger, votes can be recorded in an immutable and tamper-proof manner, ensuring that the election results are accurate and trustworthy. This can help eliminate issues related to voter fraud and increase public confidence in the electoral process.
4. Healthcare
In healthcare, DLT can be used to securely store and share medical records. By using a distributed ledger, patients can maintain control over their medical data while allowing healthcare providers to access it when needed. This can improve the efficiency of healthcare systems and ensure that patient data is protected against unauthorized access.
5. Intellectual Property and Copyrights
DLT can also be used to manage intellectual property and copyrights by providing a transparent and immutable record of ownership. Artists, musicians, and other creators can use DLT to register their works and prove ownership, reducing the risk of piracy and unauthorized use of their content.
Challenges of Distributed Ledger Technology
Despite its many benefits, there are several challenges that DLT faces:
1. Scalability
One of the main challenges of DLT, particularly in blockchain-based systems, is scalability. As the number of transactions grows, the network can become slow and inefficient. This is especially true for public blockchains like Bitcoin, where every transaction needs to be processed by every participant in the network. Solutions like sharding and Layer 2 scaling solutions are being developed to address this issue.
2. Energy Consumption
The energy consumption required by certain consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) in Bitcoin, has raised concerns about the environmental impact of DLT. Efforts are being made to develop more energy-efficient consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS), which require less computational power.
3. Regulatory Concerns
As DLT continues to gain traction, regulators are grappling with how to effectively govern and oversee decentralized systems. The lack of a central authority makes it difficult to enforce regulations, and there are concerns about how to address issues such as money laundering, fraud, and security breaches within DLT networks.
Conclusion
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a transformative innovation that has the potential to reshape industries ranging from finance to healthcare. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature provides numerous advantages over traditional centralized systems, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved data integrity.
While there are challenges to overcome, such as scalability and energy consumption, the continued development of DLT solutions promises to unlock even more possibilities. As more industries explore the benefits of distributed ledgers, it is clear that this technology will play a critical role in the future of data management and decentralized systems.








Leave A Reply