Introduction
The digital age has transformed the way we interact, trade, and share resources. Among the most groundbreaking innovations is the Peer-to-Peer (P2P) model, which allows individuals to engage in transactions directly with one another, bypassing traditional intermediaries such as banks or corporations. This decentralized approach has found applications in various sectors, including finance, technology, and even social networks.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of Peer-to-Peer systems, how they work, their benefits, and the challenges they present. Whether you’re involved in cryptocurrency trading, online lending, or simply using peer-to-peer services, understanding this model is crucial to leveraging its potential.
What is Peer-to-Peer (P2P)?
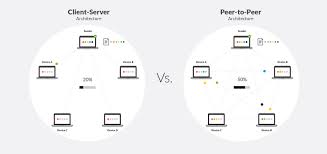
At its core, Peer-to-Peer (P2P) refers to a decentralized model in which two individuals or entities can interact and exchange value directly with one another, without the need for a central authority or intermediary. This concept has been a part of many industries, with the most well-known example being the rise of P2P networks for file sharing, such as BitTorrent.
In the context of financial services, P2P enables direct transactions between individuals, often facilitated through online platforms. This model has gained significant popularity in recent years, particularly with the rise of P2P lending, P2P cryptocurrency exchanges, and P2P payment systems.
How Does Peer-to-Peer Work?
The Peer-to-Peer model operates on the principle that two parties can transact without needing an intermediary. In traditional systems, banks or other financial institutions act as intermediaries to validate and process transactions. P2P platforms, on the other hand, leverage technology—such as blockchain, smart contracts, or simply secure communication protocols—to facilitate these direct interactions.
For example, in P2P lending, a borrower can directly obtain a loan from an individual lender through an online platform, which facilitates the connection and ensures the transaction’s security. In P2P cryptocurrency exchanges, users can directly buy or sell digital currencies with one another, often with minimal fees compared to centralized exchanges.
In P2P payments, individuals can send funds directly to others via mobile apps, bypassing traditional banks or payment processors. Services like Venmo, PayPal, and Cash App are popular examples of P2P payment systems.
Benefits of Peer-to-Peer Systems
1. Lower Costs
One of the most significant advantages of P2P transactions is the reduction in costs. Traditional systems often require intermediaries—such as banks, brokers, or payment processors—that charge fees for their services. With P2P systems, these middlemen are eliminated, meaning participants can often transact with lower fees or even for free.
For example, in P2P lending, borrowers might secure loans at more competitive interest rates since they are dealing directly with individual lenders, cutting out traditional financial institutions. Similarly, P2P cryptocurrency exchanges offer lower transaction fees compared to centralized platforms.
2. Increased Privacy and Control
By removing intermediaries, P2P systems give users more control over their transactions. In P2P payments, users don’t have to share sensitive information like bank account numbers with a third party. Instead, they can interact directly with the recipient, ensuring greater privacy.
Moreover, users can make decisions based on their terms. For instance, in P2P lending, both lenders and borrowers agree on the terms directly, including the loan amount, repayment schedule, and interest rates.
3. Decentralization
In a P2P system, there is no central authority overseeing transactions, making it a decentralized model. This is particularly important in areas like cryptocurrency, where decentralization ensures that the system remains immune to government control or interference.
Decentralization also contributes to security, as P2P platforms use encryption and blockchain technology to protect user data. In the case of P2P cryptocurrency exchanges, users retain ownership of their funds until the transaction is complete, minimizing the risk of hacks and fraud often associated with centralized exchanges.
4. Access to a Global Market
One of the most exciting aspects of P2P systems is their ability to provide global access to services. With the internet as the bridge, individuals can connect with others worldwide, bypassing the geographical limitations that traditional institutions impose.
For instance, P2P lending platforms allow individuals to lend and borrow money internationally. Similarly, P2P cryptocurrency exchanges facilitate cross-border transactions without needing a bank or third-party service, making it easier for people in underbanked or unbanked regions to access financial services.
Common Use Cases of Peer-to-Peer
1. P2P Lending and Borrowing
P2P lending platforms have become increasingly popular in recent years. These platforms connect borrowers with individual lenders who are willing to offer loans at competitive rates. Some popular P2P lending platforms include LendingClub, Prosper, and Funding Circle.
Unlike traditional financial institutions, these platforms are often more flexible in terms of lending criteria and loan amounts. Additionally, they often offer better interest rates for borrowers, as the middlemen (banks) are removed from the equation.
2. P2P Cryptocurrency Exchanges
P2P cryptocurrency exchanges allow users to trade digital currencies directly with one another, without the need for a central exchange. Platforms like LocalBitcoins and Paxful are examples of P2P exchanges where users can buy and sell cryptocurrencies directly, often with more privacy and fewer fees than centralized exchanges.
3. P2P Payments and Transfers
P2P payment apps such as Venmo, PayPal, and Cash App allow users to send money directly to others via their mobile devices. These services have become increasingly popular for personal transactions, allowing users to pay friends, split bills, or send money across borders without the need for traditional banks.
Challenges of Peer-to-Peer Systems
While P2P offers significant benefits, it also comes with certain risks and challenges:
1. Security Concerns
In P2P systems, users may be vulnerable to scams, fraud, or counterparty risks. For example, in P2P cryptocurrency exchanges, a user could be tricked into sending cryptocurrency to a scammer. Although platforms have security measures in place, users must exercise caution when transacting.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty
Since P2P systems operate outside traditional regulatory frameworks, there is uncertainty regarding how governments will handle these platforms in the future. For example, in some countries, P2P lending and cryptocurrency exchanges face regulatory scrutiny, which could lead to legal challenges for platforms and users.
3. Lack of Consumer Protection
Unlike traditional banking systems, P2P transactions are typically not insured, meaning that if a transaction goes wrong or the platform faces issues, there is little recourse for the user. This lack of consumer protection makes it important for users to thoroughly vet platforms and transactions before committing.
Conclusion
The Peer-to-Peer model has proven to be a transformative force in multiple industries, particularly in finance and digital transactions. By eliminating intermediaries, reducing costs, and increasing privacy, P2P systems offer users greater control over their financial interactions. Whether you are involved in P2P lending, cryptocurrency trading, or simply sending money through P2P payment apps, understanding how these systems work is essential to fully benefit from their advantages.
However, it is important to remain aware of the risks, such as security concerns and regulatory challenges. As the P2P ecosystem continues to grow, it will be crucial for users to stay informed and exercise caution to ensure safe and efficient transactions.








Leave A Reply