Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of blockchain technology, new innovations continue to emerge, enhancing the versatility and functionality of decentralized systems. One such innovation that has gained significant attention is hybrid blockchain. As the name suggests, a hybrid blockchain combines elements of both public and private blockchains, offering the benefits of both systems while mitigating their individual limitations. This article explores what hybrid blockchains are, how they work, and why they are gaining traction in various industries.
What is Hybrid Blockchain?
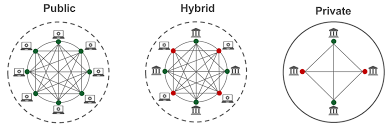
A hybrid blockchain is a type of blockchain that combines the features of both public and private blockchains. A public blockchain is an open, decentralized network where anyone can participate, view transactions, and validate blocks. On the other hand, a private blockchain restricts access, allowing only certain participants to view or validate transactions.
A hybrid blockchain allows for controlled access and permissioned operations while maintaining transparency and decentralization in specific areas. In essence, it offers the flexibility of a private network with the openness of a public one, ensuring privacy and security while benefiting from the transparency and security that public blockchains provide.
How Hybrid Blockchains Work
Hybrid blockchains are designed to address the limitations of both public and private blockchains. Here’s how they work:
- Permissioned and Permissionless Components: A hybrid blockchain typically consists of a permissioned component (similar to private blockchains) and a permissionless component (similar to public blockchains). In the permissioned portion, transactions are validated by a pre-approved group of participants, which ensures privacy and security. In the permissionless section, the data is made public, allowing anyone to access and verify it.
- Data Privacy and Security: One of the core strengths of hybrid blockchains is their ability to provide data privacy. For instance, confidential business information, intellectual property, or personal data can be kept private within the permissioned network. At the same time, the public aspect of the blockchain can allow for transparent, immutable records that anyone can audit.
- Customizable Governance: Hybrid blockchains enable organizations to define their governance structure. The public portion of the blockchain is generally used for governance transparency, while the private portion allows the organization to maintain more control over decision-making and the validation process.
- Smart Contracts and Interoperability: Smart contracts are often integrated into hybrid blockchains, facilitating automated transactions and business operations. Additionally, hybrid blockchains are designed to interact seamlessly with other blockchain systems, ensuring greater interoperability between different blockchain platforms.
Benefits of Hybrid Blockchain
- Enhanced Privacy and Security One of the most significant advantages of hybrid blockchains is the ability to maintain privacy and confidentiality while still benefiting from the advantages of blockchain technology. Sensitive data can be securely stored and managed in the private portion of the network, while the public section allows for transparency. This makes hybrid blockchains ideal for industries where data protection is critical, such as healthcare, finance, and government.
- Improved Scalability Hybrid blockchains provide scalability that neither public nor private blockchains alone can achieve. Public blockchains can struggle with transaction throughput and performance, while private blockchains may be limited by their centralization. By combining both models, hybrid blockchains allow for greater scalability without sacrificing decentralization or security.
- Flexibility in Governance Hybrid blockchains offer flexible governance models, enabling organizations to retain control over sensitive information while maintaining transparency in certain aspects of the network. This is particularly useful for enterprises and governments that require a balance between privacy and accountability.
- Increased Trust and Transparency While hybrid blockchains maintain private data in some cases, they also promote transparency in specific parts of the system. This transparency fosters trust among users and ensures that all actions taken on the blockchain are immutable and verifiable. For example, in supply chain management, the public aspect of the blockchain allows for tracking goods in real time, ensuring authenticity and preventing fraud.
- Interoperability Hybrid blockchains are designed to work seamlessly with other blockchain networks, allowing for greater interoperability. This feature is essential as blockchain ecosystems grow and diversify, allowing businesses to connect different networks without encountering the challenges of siloed systems.
Use Cases for Hybrid Blockchain
- Supply Chain Management One of the most promising applications of hybrid blockchain is in supply chain management. Companies can use the private section of a hybrid blockchain to store sensitive data, such as supplier contracts or pricing information, while using the public portion to track the movement of goods, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. By doing so, companies can optimize their operations, improve traceability, and prevent fraud.
- Financial Services In the financial sector, hybrid blockchains can be used to create secure, transparent, and efficient platforms for cross-border payments, asset management, and regulatory compliance. Financial institutions can leverage the private section of the hybrid blockchain to protect customer data, while the public portion can be used for transaction validation and auditing, ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Healthcare The healthcare industry deals with sensitive patient data that must be securely stored and shared. A hybrid blockchain offers a solution by allowing healthcare providers to maintain the privacy of patient records in the private section of the blockchain, while the public section can be used for verifying the authenticity of medical credentials, prescriptions, and research data. This ensures both security and transparency in the healthcare ecosystem.
- Government and Voting Systems Hybrid blockchains can be used in governmental applications such as voting systems, where transparency and security are paramount. Voter identities and ballots can be kept private in the permissioned network, while the voting results can be made publicly available in the permissionless network to ensure transparency and prevent manipulation. This solution helps to increase voter trust and participation.
- Intellectual Property and Content Protection Intellectual property (IP) rights can be easily protected using hybrid blockchain technology. Content creators can store their work in the private section of the blockchain to protect their IP rights while using the public portion to share information about the ownership and licensing terms. This ensures that creators can maintain control over their work while allowing for easy verification by third parties.
Challenges and Considerations
While hybrid blockchains offer many advantages, they also present some challenges. One of the key concerns is the complexity of setting up and maintaining such systems. The integration of both public and private components requires robust technical expertise and careful planning. Additionally, hybrid blockchains must strike a balance between decentralization and centralization, which may be difficult to achieve in some cases.
Regulatory challenges also remain a significant concern, particularly when it comes to ensuring compliance with data privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Organizations using hybrid blockchains must ensure that they comply with relevant regulations while also taking full advantage of the benefits blockchain provides.
Conclusion
Hybrid blockchain technology represents a new frontier in the world of decentralized systems. By combining the advantages of public and private blockchains, it offers enhanced privacy, security, scalability, and flexibility. Hybrid blockchains are poised to transform industries such as finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and government by providing a solution that balances transparency with privacy. While challenges remain in terms of implementation and regulation, hybrid blockchains hold the potential to become a key component of the blockchain landscape in the years to come.








Leave A Reply