In the digital age, decentralization has become a pivotal concept, revolutionizing how we interact with systems and assets across various industries. From finance to technology and even governance, decentralization is pushing the boundaries of traditional models by offering greater transparency, security, and control to users. In this article, we’ll explore what decentralization is, how it works, its advantages, and the potential challenges that come with it.
What is Decentralization?
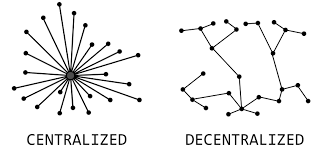
At its core, decentralization refers to the distribution of authority, control, and data across multiple participants or nodes in a network, rather than being concentrated in a single central entity. In centralized systems, a single organization or authority controls operations, resources, and decision-making. In decentralized systems, however, control is spread across a network, with no single point of failure.
Blockchain technology, the backbone of many cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, is the most prominent example of decentralization in practice. Instead of relying on a central authority like a bank or government to verify and process transactions, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network where multiple participants maintain and verify the ledger independently. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, thereby reducing costs and improving security.
How Does Decentralization Work?
Decentralization typically works through a distributed network of nodes, which can be any participant or device connected to the system. These nodes collectively work to process and validate transactions or actions. In the case of blockchain, these nodes ensure that every transaction is legitimate, recorded, and irreversible.
For example, in a decentralized cryptocurrency network like Bitcoin, each transaction is verified by a network of miners, rather than a central authority. These miners use computational power to solve complex mathematical puzzles that validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Once the transaction is validated, it is recorded and made publicly available, ensuring transparency and security.
Key principles that underpin decentralization include:
- Distributed Control: No single entity or individual has full control over the system. Control is distributed among network participants.
- Transparency: Actions taken within decentralized systems are usually transparent and publicly verifiable, making it difficult for bad actors to manipulate or alter the system.
- Security: With no central point of failure, decentralized systems are inherently more secure from hacks or attacks. The decentralized nature makes it challenging for adversaries to take control or disrupt the network.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Interaction: Participants in a decentralized system can interact directly with one another, reducing the need for intermediaries and fostering more efficient transactions.
Advantages of Decentralization
1. Increased Transparency
One of the main benefits of decentralization is the increased transparency it offers. In decentralized systems, actions are recorded on a publicly accessible ledger that cannot be tampered with. In blockchain, for instance, every transaction is visible to all participants, allowing them to independently verify the system’s integrity.
This transparency helps in creating trust among users since everyone can see and audit the activity happening on the platform. This is particularly crucial in industries like finance, where trust and accountability are paramount.
2. Enhanced Security
In centralized systems, all data is stored in one location, which creates a single point of failure. If a hacker gains access to the centralized server, they can potentially compromise the entire system. However, in a decentralized network, data is distributed across multiple nodes, making it significantly harder to attack or manipulate.
This makes decentralized systems, particularly blockchain networks, more secure against attacks and data breaches. Even if a portion of the network is compromised, the system as a whole can continue to function correctly.
3. Reduced Censorship and Manipulation
Decentralization removes the power from a single entity, such as a government, corporation, or bank, that could potentially manipulate or censor the system. In a decentralized network, no single party can control the rules or decisions, which helps protect users from censorship and other forms of manipulation.
For example, in traditional banking systems, transactions can be blocked or delayed by financial institutions based on internal policies or government regulations. In contrast, decentralized networks, like those built on blockchain, operate independently, allowing users to freely send and receive transactions without fear of censorship.
4. Empowering Individuals
Decentralization empowers individuals by giving them control over their assets, data, and actions. With decentralized platforms, users are not dependent on intermediaries or centralized authorities to facilitate their transactions or access their data. This autonomy allows individuals to interact more freely and make decisions without the influence of a central authority.
For example, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms enable users to access financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without the need for traditional banks. This democratizes access to financial services and opens up opportunities for individuals who are excluded from the conventional financial system.
Applications of Decentralization
1. Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of decentralization is the cryptocurrency market. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others are built on decentralized blockchain technology. These digital currencies allow individuals to send and receive funds without the need for intermediaries like banks, making the process faster, cheaper, and more secure.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging sector within the cryptocurrency space that aims to recreate traditional financial services using decentralized technologies. DeFi platforms offer services such as lending, borrowing, yield farming, and insurance, all without relying on traditional financial intermediaries. DeFi protocols are powered by smart contracts, which automatically execute transactions based on predefined conditions.
3. Supply Chain Management
Decentralization can significantly enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains. By using blockchain, companies can track the origin, movement, and condition of goods at every step of the supply chain. This helps reduce fraud, ensures product authenticity, and provides customers with greater visibility into the products they purchase.
4. Voting Systems
Decentralized voting systems are being explored as a way to reduce election fraud and enhance transparency. Blockchain-based voting systems could allow individuals to cast their votes securely and anonymously, while also providing a transparent and verifiable record of the results. This could significantly improve the integrity of electoral processes.
Challenges of Decentralization
While decentralization offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its set of challenges:
1. Scalability
Many decentralized systems, particularly blockchains, face scalability issues. As the number of users and transactions increases, the network can become congested, leading to slower transaction times and higher fees. Solutions such as sharding and layer-2 protocols are being developed to address scalability challenges, but it remains an ongoing issue.
2. Governance
Decentralized systems often struggle with governance. While decentralization gives users more control, it can also lead to decision-making challenges. Without a central authority, reaching consensus on network upgrades or protocol changes can be difficult and time-consuming. Governance models like Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are being created to address these issues, but effective governance remains a complex challenge.
3. Regulation and Legal Issues
The lack of regulation in decentralized systems can lead to legal uncertainties. Since no central authority governs these networks, it can be difficult to enforce laws or resolve disputes. This lack of regulation also opens up the potential for fraud, scams, and illegal activities, particularly in the cryptocurrency space.
Conclusion
Decentralization is a transformative concept that is reshaping how we approach everything from finance to governance. By increasing transparency, enhancing security, and reducing reliance on intermediaries, decentralized systems are creating more efficient, equitable, and autonomous ways for individuals to interact with the digital world. However, as with any emerging technology, decentralization faces challenges related to scalability, governance, and regulation.
Despite these hurdles, decentralization remains a powerful force driving innovation. As the technology evolves, its potential to disrupt industries and provide a more secure, transparent, and fair future is immense. By embracing decentralization, we are moving towards a world where power is distributed more evenly, and individuals have greater control over their assets and data.








Leave A Reply