In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, virtual smart contracts are emerging as one of the most exciting innovations. These digital agreements are transforming how parties engage in transactions, providing a secure, transparent, and automated way to execute contracts without the need for intermediaries. In this article, we’ll explore what virtual smart contracts are, how they work, and the significant impact they’re having on various industries.
What Are Virtual Smart Contracts?
A virtual smart contract is a self-executing contract where the terms of the agreement are written directly into lines of code. The contract’s execution is triggered automatically when predefined conditions are met, and once the terms are fulfilled, the contract is executed without the need for manual intervention.
Unlike traditional contracts that require legal or third-party intermediaries to enforce the terms, virtual smart contracts operate autonomously on blockchain networks. The most common platform for developing and executing these contracts is the Ethereum blockchain, which supports smart contracts through its built-in programming language, Solidity.
Key Features of Virtual Smart Contracts
- Self-execution: Once the conditions are met, the contract automatically performs the agreed-upon actions.
- Transparency: All actions and terms of the contract are visible on the blockchain, ensuring trust between parties.
- Immutability: Once deployed, the code in a smart contract cannot be altered, ensuring that all parties are held to the original terms.
- Security: Virtual smart contracts are cryptographically secured, making them resistant to fraud or tampering.
- Decentralization: These contracts operate on decentralized blockchain networks, removing the need for intermediaries.
How Do Virtual Smart Contracts Work?
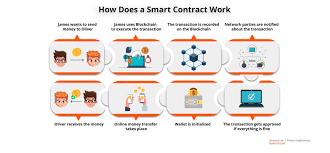
The process of creating and executing a virtual smart contract is relatively straightforward, but it requires a solid understanding of blockchain technology and programming. Here’s an overview of how they function:
- Creation: The contract is created using programming languages like Solidity (on Ethereum), which defines the terms and conditions of the contract. The code can be written to perform specific tasks, such as transferring funds or triggering an action once certain criteria are met.
- Deployment: After coding the smart contract, it is deployed to the blockchain. Once deployed, the contract is immutable, meaning it cannot be altered. It is also publicly accessible, allowing all relevant parties to verify the terms.
- Execution: When the predefined conditions of the contract are met, such as the completion of a transaction or delivery of goods, the contract executes the agreed-upon actions automatically. For example, if the contract involves the transfer of cryptocurrency, it will automatically execute the transfer once the terms are fulfilled.
- Completion: Once the contract has executed its terms, it is considered completed. Because the blockchain records all actions, the history of the contract and its execution remains permanently visible to all involved parties.
Benefits of Virtual Smart Contracts
The advantages of using virtual smart contracts are numerous, particularly in industries where automation, transparency, and security are critical. Here are some key benefits:
1. Increased Efficiency
Virtual smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing the time it takes to execute agreements. The process is automated, which speeds up transactions and reduces delays. In industries such as real estate, where paperwork and verification can take time, virtual smart contracts streamline the entire process, making it faster and more efficient.
2. Cost Reduction
By removing the need for third-party intermediaries, such as lawyers, notaries, or banks, virtual smart contracts reduce transaction fees and administrative costs. This makes them an attractive option for businesses looking to cut overhead costs while improving the speed and efficiency of their operations.
3. Transparency and Trust
The transparency of blockchain technology ensures that all parties involved in a virtual smart contract can independently verify the terms and execution of the contract. This builds trust, as no party can alter the terms once the contract is deployed.
4. Security
Virtual smart contracts are secured by blockchain’s cryptographic methods, making them highly resistant to fraud or tampering. Once a contract is executed, it is irreversible, providing both parties with a sense of security that the contract terms cannot be changed or disputed later.
5. Reduced Human Error
Since virtual smart contracts are automated and require no manual intervention, the likelihood of human error is significantly reduced. This is particularly beneficial in industries like supply chain management, where tracking goods and verifying contracts manually can lead to mistakes.
Applications of Virtual Smart Contracts
Virtual smart contracts are finding applications across a wide range of industries. Below are some notable areas where they’re making a significant impact:
1. Finance and DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
In the world of finance, DeFi platforms leverage virtual smart contracts to create decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading systems. By automating the process and removing intermediaries, DeFi platforms reduce the cost of financial services and make them more accessible. Virtual smart contracts enable transparent and secure transactions, such as token swaps and liquidity pool management.
2. Real Estate
Virtual smart contracts can revolutionize real estate transactions. Instead of relying on multiple parties to process paperwork, validate ownership, and transfer funds, smart contracts can automate the entire process. From the moment a property is listed, smart contracts can handle everything from price negotiation to escrow, and the transfer of ownership once payment is received.
3. Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, virtual smart contracts can track goods from the manufacturer to the consumer. By using smart contracts, companies can verify every step of the supply chain, ensuring that goods are delivered as agreed, and automating payments once the goods are received.
4. Insurance
Insurance policies can also benefit from virtual smart contracts. For example, smart contracts could automatically trigger payouts in the event of an accident or natural disaster based on predefined conditions. This automation reduces the need for claims adjusters and accelerates the claims process.
Challenges of Virtual Smart Contracts
While virtual smart contracts offer many benefits, they are not without challenges. Some of the most common obstacles include:
1. Technical Complexity
Creating and deploying smart contracts requires expertise in programming and blockchain technology. Without skilled developers, there is a risk of bugs, errors, or vulnerabilities in the code.
2. Legal Recognition
Despite the growing use of virtual smart contracts, many legal systems have yet to fully recognize their enforceability. Although smart contracts are gaining traction, their legal status can vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
3. Irreversible Transactions
One of the features of virtual smart contracts is that once they are deployed and executed, they are immutable. While this is an advantage in many cases, it can also be a disadvantage if a mistake is made. If an error occurs in the contract’s code, there’s no way to undo or amend the transaction once it’s completed.
Conclusion
Virtual smart contracts are poised to revolutionize the way we execute and enforce agreements. With their potential to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and provide unparalleled transparency, these digital agreements are becoming increasingly relevant in industries such as finance, real estate, supply chain management, and insurance. As the technology evolves, the adoption of virtual smart contracts will likely continue to expand, offering new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.
Despite challenges such as technical complexity and legal hurdles, the benefits of virtual smart contracts are clear. They promise to change the landscape of how transactions and agreements are conducted in the digital age, paving the way for a more automated, secure, and decentralized future.








Leave A Reply