The Lightning Network, a groundbreaking layer-2 solution for Bitcoin, has emerged as a pivotal innovation in the cryptocurrency space. Designed to address Bitcoin’s scalability limitations, this decentralized network enables near-instant, low-cost transactions while maintaining the security and decentralization of the Bitcoin blockchain. In this article, we delve into the core principles, real-world applications, and future potential of the Lightning Network, exploring how it’s reshaping the way we use Bitcoin.
Understanding the Lightning Network: A Layer-2 Marvel
The Lightning Network operates by shifting transactions off the Bitcoin blockchain and into off-chain payment channels. These channels allow users to conduct multiple transactions without broadcasting each one to the blockchain, significantly reducing congestion and fees. For instance, while Bitcoin’s base layer processes around 7 transactions per second (TPS), the Lightning Network theoretically supports millions of TPS. This scalability makes it ideal for micropayments, such as buying a cup of coffee or tipping content creators, where traditional blockchain fees would be prohibitive.
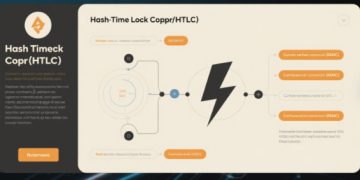
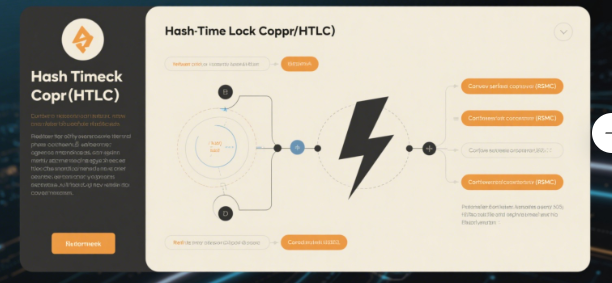
The network relies on two key mechanisms: Hashed Timelock Contracts (HTLCs) and Recoverable Sequence Maturity Contracts (RSMCs). HTLCs enable trustless transactions between parties who don’t share a direct channel by routing payments through intermediary nodes, forming a vast interconnected network. RSMCs ensure funds are protected by allowing participants to update channel balances without needing blockchain confirmation.
How the Lightning Network Works: From Channels to Global Connectivity
- Channel Creation: Users open a payment channel by locking Bitcoin into a multisig address. This initial on-chain transaction establishes the channel’s liquidity.
- Off-Chain Transactions: Within the channel, participants can send an unlimited number of transactions instantly, updating balances through signed messages.
- Settlement: When the channel closes, the final balance is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring all off-chain transactions are validated.
A critical feature is routing, where nodes act as intermediaries to connect users indirectly. For example, if User A has a channel with Node B, and Node B has a channel with User C, User A can send funds to User C through Node B, with the network automatically selecting the optimal path. This peer-to-peer infrastructure has grown exponentially, with over 1 million nodes and 700,000 channels by 2025, locking more than 5,400 BTC.
Real-World Applications: Beyond Bitcoin’s Limitations
The Lightning Network’s scalability and low fees have unlocked diverse use cases:
1. Micropayments and Instant Gratification
Platforms like Tippin.me allow users to tip content creators on social media with fractions of a cent, while streaming services like BitPay enable real-time Bitcoin subscriptions. In Mexico, retail giant Grupo Salinas integrated Lightning payments across its businesses, including supermarkets and sports clubs, driving mass adoption.
2. Cross-Border Remittances
Traditional remittances are slow and costly, but Lightning Network reduces fees to near-zero and settlement times to minutes. Projects like Strike are leveraging this to connect unbanked populations in Africa and Southeast Asia.
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
By integrating with side chains like Rootstock and rollups like Merlin Chain, the Lightning Network allows Bitcoin to participate in DeFi activities such as lending and liquidity mining. This bridges Bitcoin’s store-of-value narrative with Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem.
4. Social and Creative Industries
The Nostr protocol uses Lightning to enable censorship-resistant social media, where users pay for content directly via micropayments. Artists like Emily in New York use Lightning to let viewers “unlock” dynamic NFT art with small payments.
Challenges and Innovations Ahead
While the Lightning Network has made significant strides, it faces challenges:
- Liquidity and Usability: Users must pre-fund channels, which can be a barrier for casual users. Solutions like Lightning Service Providers (LSPs) aim to simplify this by managing channels on behalf of users.
- Privacy: Current routing exposes transaction paths. Upgrades like Taproot and zero-knowledge proofs are being developed to enhance privacy by obfuscating transaction details.
- Centralization Risks: A few large nodes dominate routing. Projects like Arbitrum are exploring decentralized incentives to distribute network control.
Looking ahead, channel splicing will allow users to adjust channel balances without closing them, improving liquidity management. Additionally, integrating stablecoins like USDT-L on Lightning will expand its utility for everyday transactions.
The Future of Bitcoin: A Scalable, Global Payment Network
The Lightning Network is not just a solution—it’s a paradigm shift. By enabling Bitcoin to handle millions of transactions efficiently, it bridges the gap between Bitcoin’s role as “digital gold” and its potential as a global payment system. As adoption grows, we’re witnessing a transition from niche crypto enthusiasts to mainstream businesses and institutions embracing Lightning-powered payments.
For developers and businesses, the Lightning Network offers a playground for innovation. From decentralized exchanges like LN Markets to hardware solutions like Fi5Box, the ecosystem is thriving. And with ongoing advancements in privacy and usability, the Lightning Network is poised to become the backbone of a faster, more inclusive financial infrastructure.
At Bitora, we’re committed to tracking the Lightning Network’s evolution and providing insights into its impact on the crypto landscape. Stay tuned for updates on how this transformative technology continues to shape the future of Bitcoin and decentralized finance.
For the latest news and analysis on Lightning Network and other blockchain innovations, visit Bitora—the ultimate destination for crypto enthusiasts and professionals.