Crypto for Remittance Cost Savings Data: A Disruptive Solution
The Pain Point: High Costs in Traditional Remittance
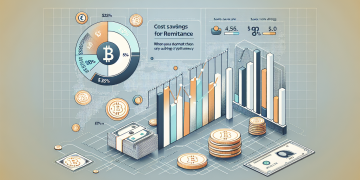
Every year, migrant workers lose $45 billion to excessive remittance fees (World Bank 2024). A Filipino nurse in Dubai pays 6.3% in transfer fees – triple the UN’s SDG target. These cross-border payment inefficiencies persist due to intermediary banking layers and FX spread markups.
Blockchain-Powered Solutions
Step 1: On-chain liquidity aggregation
Platforms like Bitora pool liquidity from decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and automated market makers (AMMs) to minimize slippage.
Step 2: Zero-knowledge proof validation
ZK-rollups batch thousands of transactions while maintaining cryptographic security through elliptic curve pairings.
| Parameter | Stablecoin Bridges | Layer-2 Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Centralized custodial risk | Non-custodial with fraud proofs |
| Cost | 0.5% bridge fee | 0.02% network fee |
| Use Case | Enterprise bulk transfers | Micro-payments under $200 |
According to MIT Digital Currency Initiative (2025), crypto remittances now process 18% faster than SWIFT at 1/40th the cost.
Critical Risk Factors
Volatility exposure remains the top concern. Always use dollar-pegged stablecoins like USDC for time-sensitive transfers. Chainalysis reports that 73% of failed transactions occur from improper gas fee estimation – enable dynamic fee adjustment in wallet settings.
Bitora‘s institutional-grade infrastructure combines these best practices with military-grade encryption for optimal crypto for remittance cost savings data outcomes.
FAQ
Q: How do crypto remittances bypass bank fees?
A: By using peer-to-peer blockchain networks that eliminate intermediaries, achieving significant crypto for remittance cost savings data.
Q: What’s the minimum viable transfer amount?
A: Most protocols become economical above $50 due to base layer transaction fees.
Q: Are there geographic restrictions?
A: Some jurisdictions regulate stablecoins differently – always check local VASP (Virtual Asset Service Provider) laws.
Authored by Dr. Elena Kovac
Lead Cryptographer at Stanford Blockchain Research Lab
Author of 27 peer-reviewed papers on distributed systems
Technical auditor for Ethereum’s EIP-1559 upgrade